红泥泵白皮书
Mt Rosser池塘
修复项目泥泵测试-发现
文件控件shet
| 客户端 | 里安丁托阿尔康 | |||||
| 项目标题 | Rio丁托Alcan排除资产补救 | |||||
| 文档标题 | 泥泵测试-结果 | |||||
| 文件号 | MDE0182RP0038WPR | |||||
| 文档编译 | DAS | TOC测试 | 文本翻译 | 表列表 | 图列表 | 号联想 附录 |
| 一号 | 一号 | 16 | 0 | - | - | |
| 公元前 | 状态 | 发件人 | 评审由 | 核准程序 | 原创办公 | 问题日期 |
| D01 | 草稿 | WOSMOND | Cmason,Rapp | 西码头 | 11年10月22日 | |
| F01 | 终极 | WOSMOND | C马松 | WOSMOND | 西码头 | 11月15日 |
一. 导言
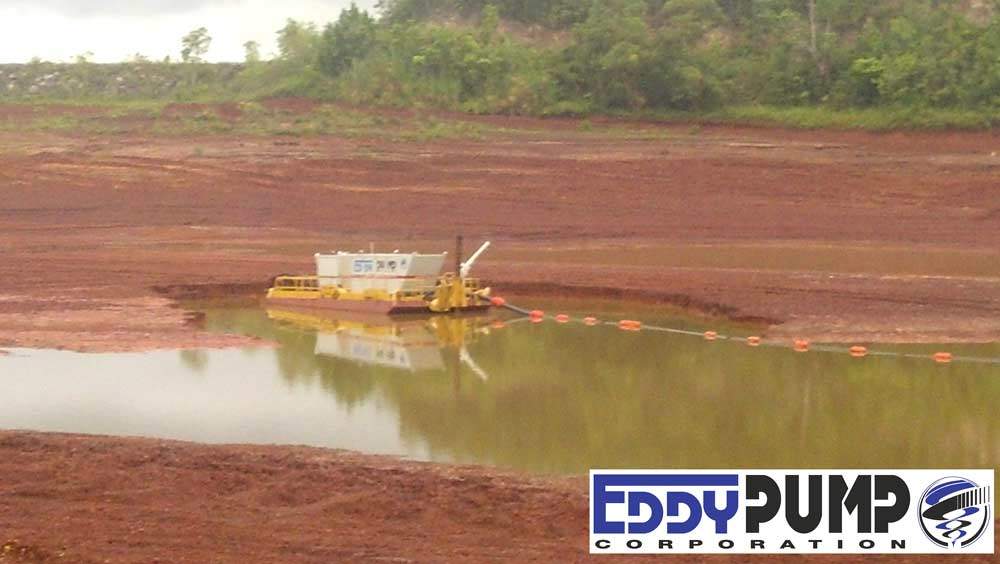
mt RosserPond是一个铝土残留物(红泥)尾矿大坝,位于牙买加Ewerton镇北面Diablo山
The "pond" is actually a man made dam which covers an area of about 40ha and has rockfill embankments of up to 53m high along the southern side that forms the impoundment. It initially constructed in 1959 to act as a tailings pond to take the bauxite residue (red mud) from the Ewarton Plant situated about 5km away and 300m lower. The red mud was pumped as a slurry comprising about 20% solids to the pond over a period of about 32 years up to 1991 when the pond was replaced by the Charlemount Mud Stacking and Drying Facility. During this period the pond embankments (referred to as dams), were raised up to 7 times providing a final crest elevation of 472m. The pond was however never filled to its final design capacity and the mud beach level remained at about 469m and the central area about 458m leaving a concave depression which held about 1.4mil m3水加高pH和某些腐蚀性内容
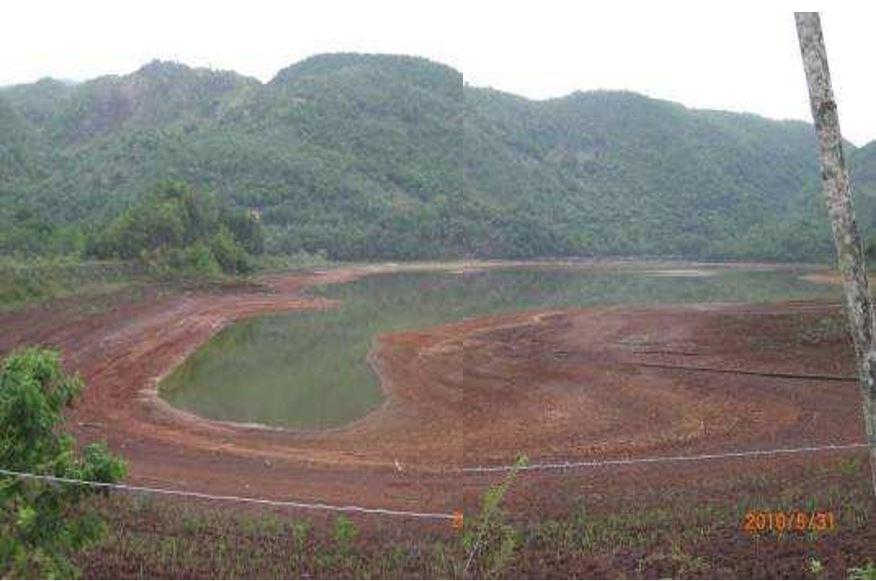

池塘修复计划包括清除池塘水并重定位泥面免费排水,以便稳定并播种。 约500 000米3of mud will need to be moved over a distance of up to 1km in order to create the required profile. Due to the very soft nature of the surface muds (shear strength of less than 3kPa) its bearing capacity is less than 20kPa hence it is not accessible using even modified earthworks equipment. In addition, the muds are thyrotrophic and under any vibration or shear loading, rapidly liquefy resulting in significant reduction in shear strength and loss of bearing capacity. Using conventional earthmoving equipment would therefore require extensive "floating" haul roads with a high risk of machinery getting stuck or entire plant loss and risk to personnel. It was therefore decided to investigate the possibility of pumping the in-situ red mud.
泥泵测试评估使用此技术大规模泥流的可行性 红泥不常见,泥浆最初抽到Mt Rosser池塘
除泥泵外,测试内容包括填充三大小型地理管评估性能
项目引用 :AUM0894牙买加HSEQ工作包refJWP#11001
1.1AIM法庭
水泵试验的主要目的是确定泥能按原状泵化,如果没有,需要水量和水含量变化如何影响泵速率
关联到:
- 渐渐理解在这些条件下抽水的困难
- 了解泵区周围泥土行为
- 评估泥土沉入水中后如何反应
地球管的主要目的就是评估管子如何控制泵泥和它们用时反应
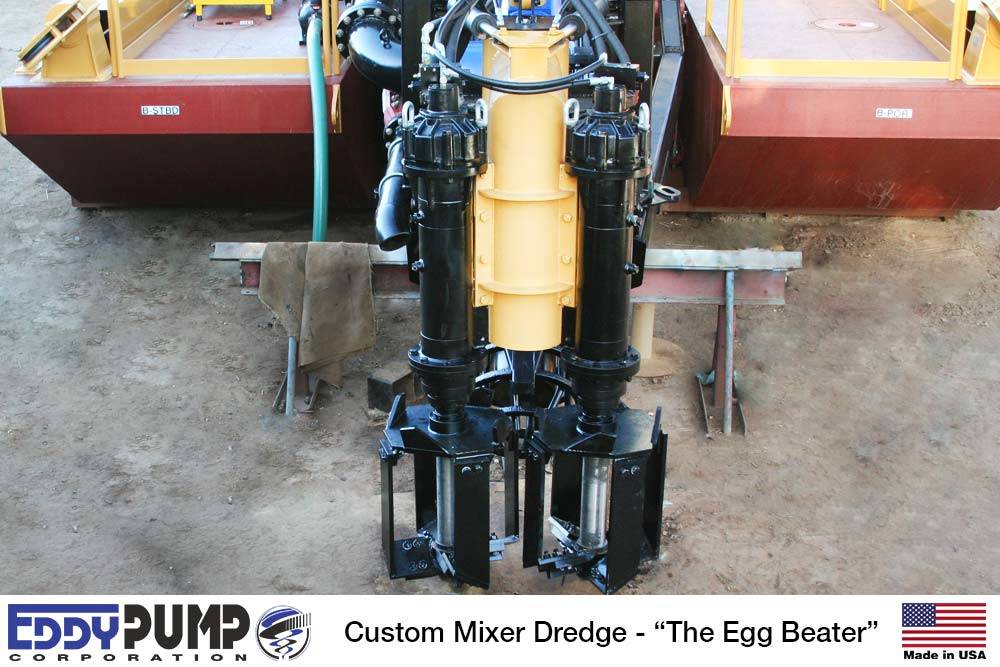
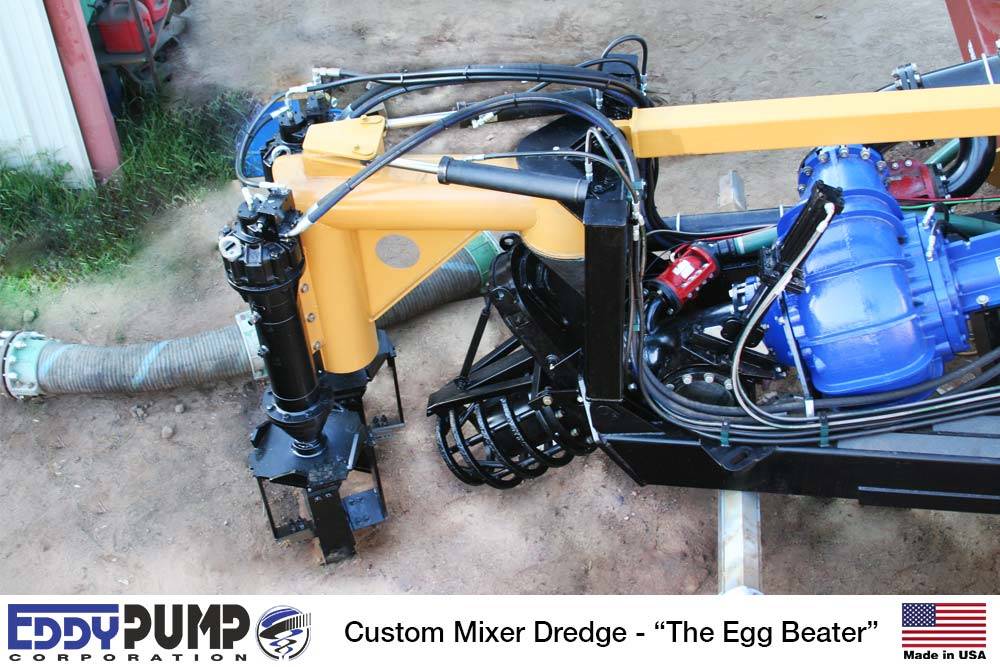
2设备使用
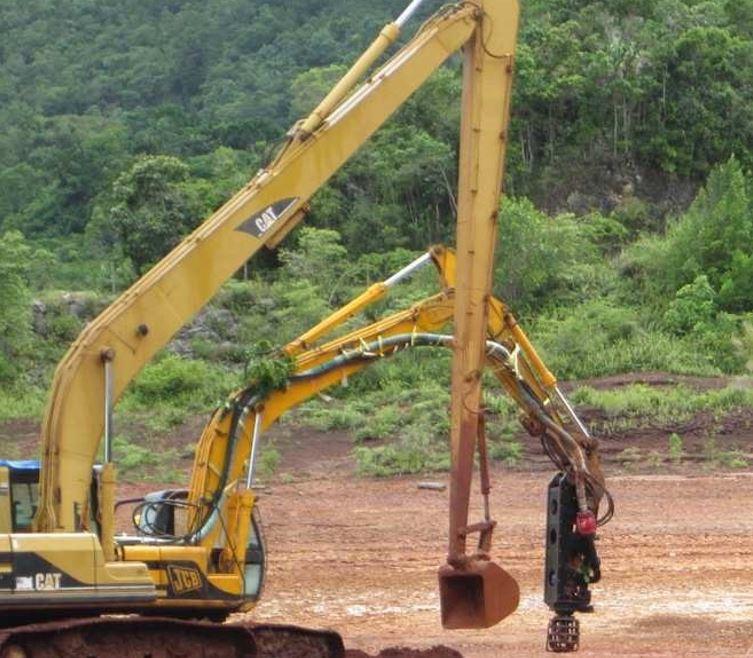
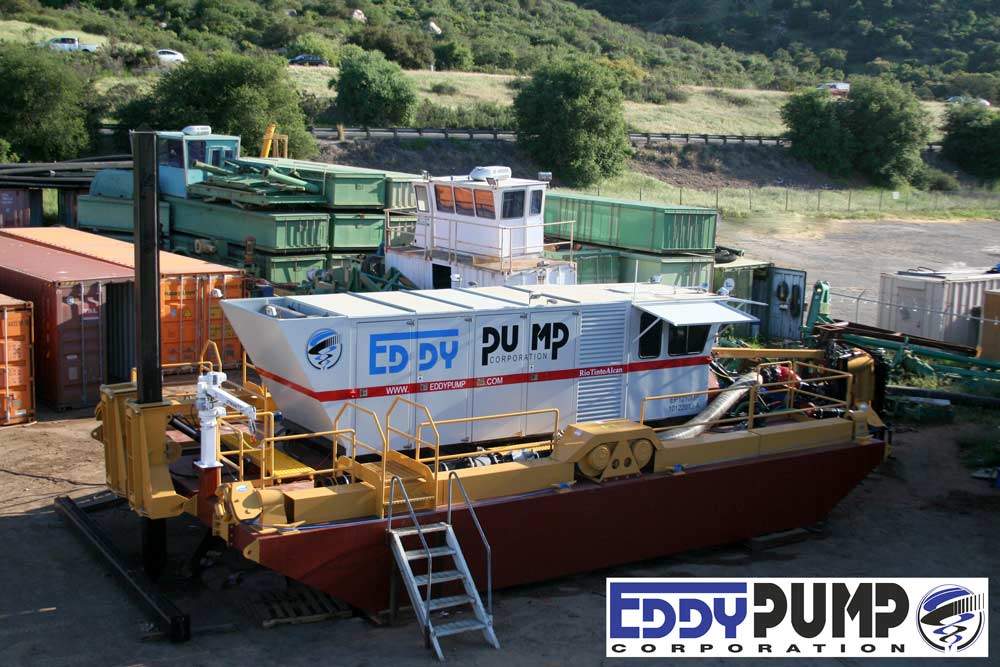
The mud pumping trial was undertaken using a 4" EDDY Pump. This pump was recommended due to its ability to handle variable solids and robust operating mechanism. The pump unit incorporated a hydraulic drive and cutter head. The unit was mounted onto the boom of a JCB 220 excavator which also supplied the hydraulic feed to power the pump for the required range of 30-40 GPM at 3,500 to 4,000 psi (2428MPa). The cutter head was powered by a standalone hydraulic power unit capable of providing the required 30gpm at 200psi (1.9 l/s at 13.8MPa). If mounted on a 30-ton excavator with a System 14 hydraulic system and dual auxiliary feeds to the boom, all necessary hydraulic power for the pump and cutter head can be supplied by the excavator. This equipment was however not available at the time in Jamaica.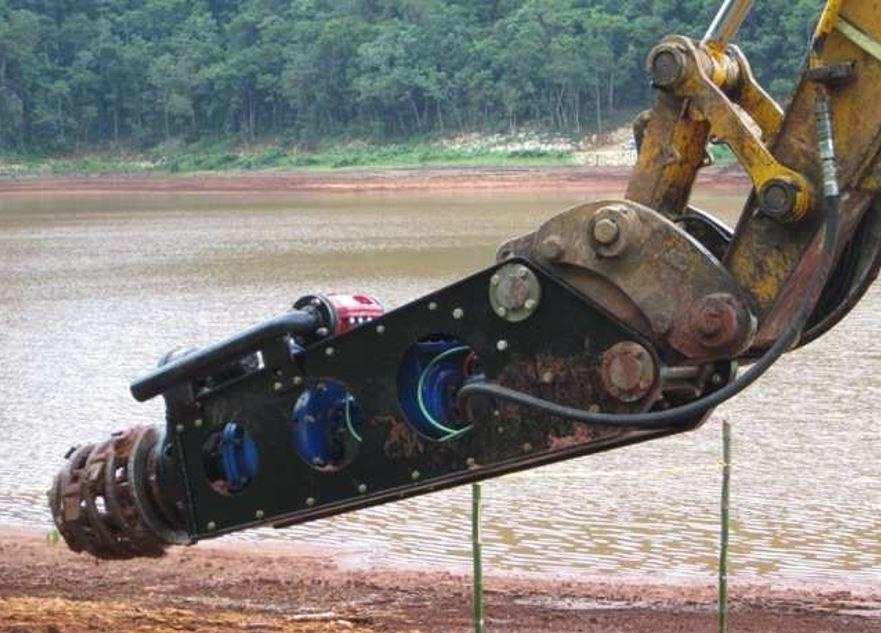
除挖掘机上安装泵外,用长距离挖掘机(CAT325)向切割机头移动泥浆,并松绑泥土和混合加水方便抽水
抽泥前,泥泵以回流模式操作泵。当回循环模式时,泵材料会转置到泵上安装短排管上并转回切头这一行动会帮助鼓动和搅乱泥巴

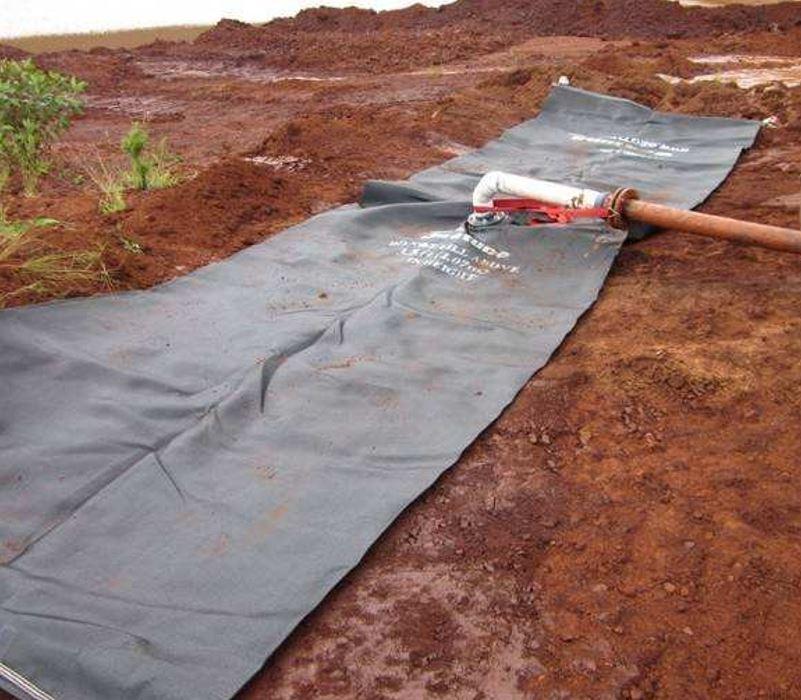
地球管测试长6m和高1m(填充),由腾卡特提供。 管子由编织聚点-GT1000M制成并有中央顶填点。 并提供了装有聚合测试集的小袋,但这次没有试用

3材料属性
2004年对Mt Rosser池塘中的泥土进行了地质土壤调查,调查显示材料主要是粘泥泥沙约13%、粘土29%和泥沙58%使用传统筛析和水力计。Atterberg限值显示材料介于高塑性粘土之间。但泥土分布于湖中并垂直变化主要是沉积过程和排出点的结果。靠近排出点,教程材料先解决,精度材料最远散至池子对面,结果见图4.1
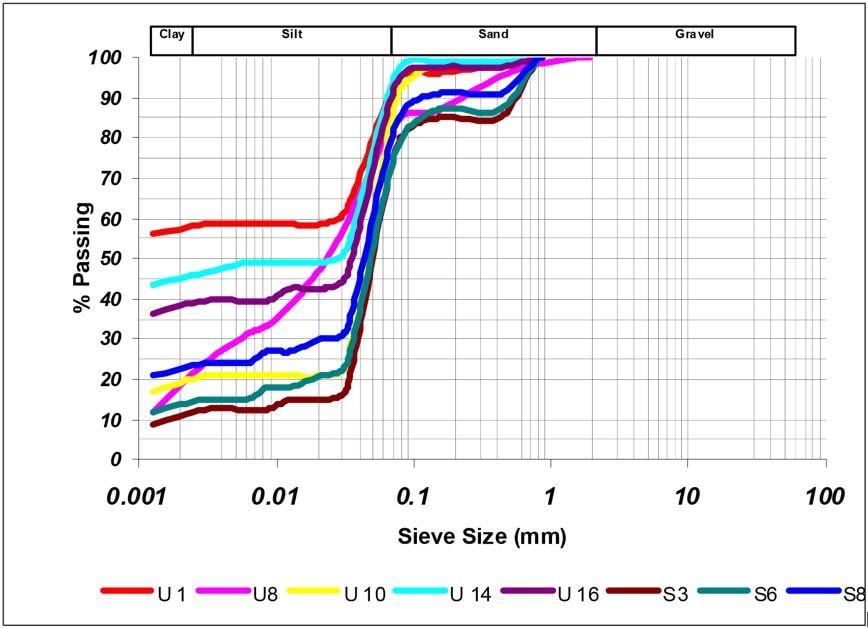
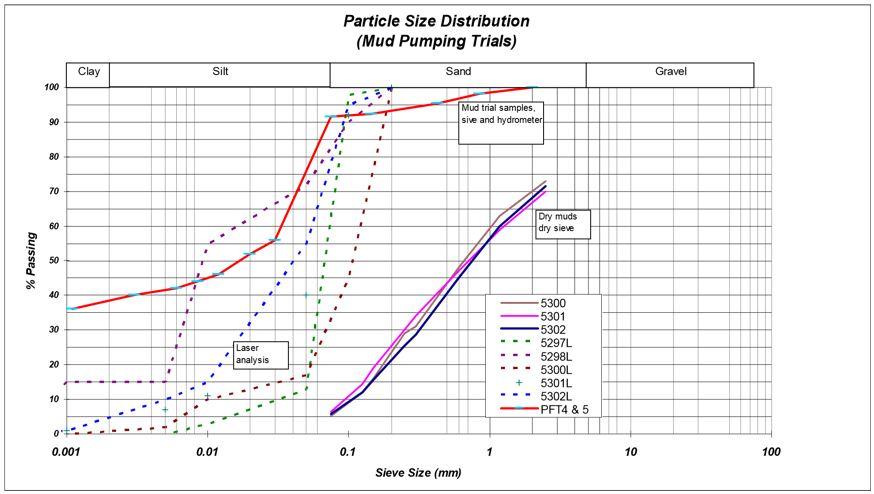
在今年早些时候测试了更多的泥样本,因为标准土力测试显然无法提供精美材料的精确评估,这一点在干筛检验中特别明显,测试显示物色优沙(见样本5300、5301和5302结果图4.2)。
附加测试包括使用激光粒子分析器进行分级结果表明泥块主要是石板,尽管淤泥百分比介于30%至80%不等,物料多沙或粘土多(达15%粘土)。下图4.2显示样本归结为“L”。
泥池内取泥量测试水下从100%到150%不等(50%到40%固态 ) 。 泵测试点的泥量检验为137%(42%固态 ) 。
剪裁强度通常很低,从1kPa到6kPa等深层相加
PH介于10.3至11.7之间(除11.2外),先前测试显示表层泥有低pH测试时深达2.5m的泥混在一起,因此无法确定pH分层
4发现
41MUD泵
初始抽水问题主要因挖掘机功耗不足诊断为液压泵问题并替换挖掘机。切割机头(也作用保护摄取量)偏盲泥块(Photo5.1),也没有提供足够的扰动性液化泥块。这通过在旋转切割机头上加插“Stirrs”(2钢环焊接双侧)和comb(Photo5.2)来部分解决,以保持切割机头空格开关
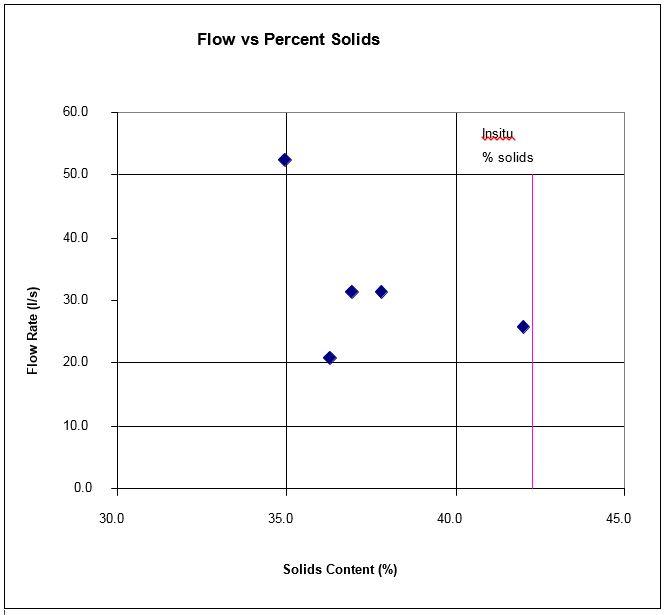
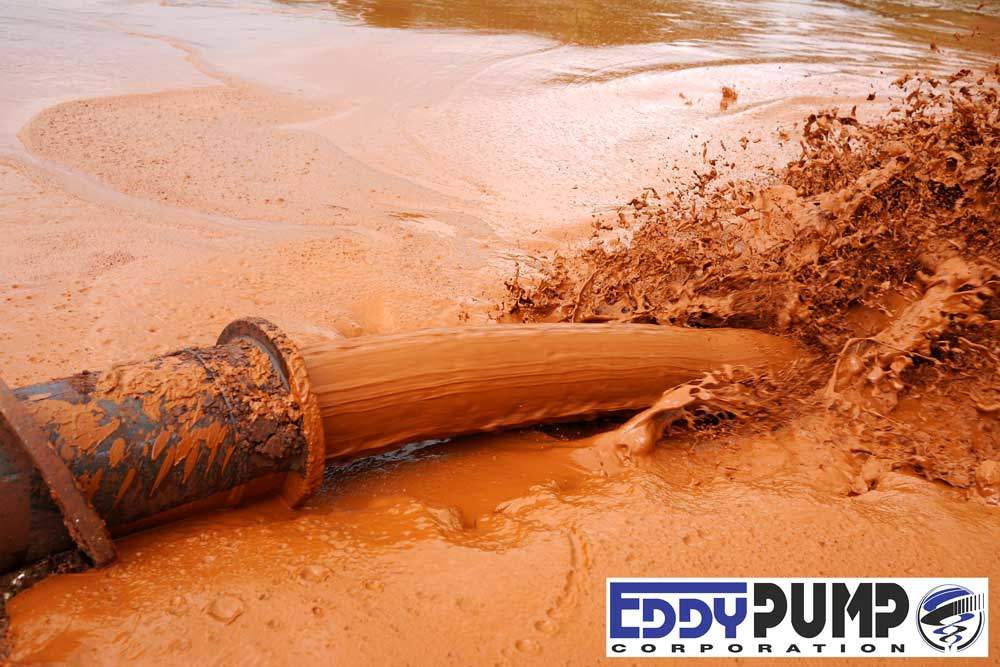
Mud pumping rates varied from 21 l/s to 52 l/s (332 – 824gpm) and it was clearly visible that the more liquid the muds were the higher the pump rate was. Samples were taken at different discharge rates and moisture content and percent solids determined by laboratory testing. The results are plotted in Figure 5.1 and although scattered, do give an indication of the effects of solids content on flow rates. The natural moisture content of the muds (insitu) at the test location was 137%, or 42% solids. This is shown in Figure 5.1 as a vertical line. Pumping muds close to the percent solids was achieved although flow rates were low.
长距离挖掘机用来松绑泥巴,水从池塘抽水3号泵挖掘,长距离挖掘泥巴混入水中帮助初始冲压泵进程,并曾为地表下1米至2米热泥泵,但发现深泥往往卷积性,这将大大减少或停止流水量要求泵升入薄泥或返回回弧模式或完全回租模式,因此泵排出极不一致性,因为吸附位置需要不断调整以图适当排出并同时抽出最厚泥
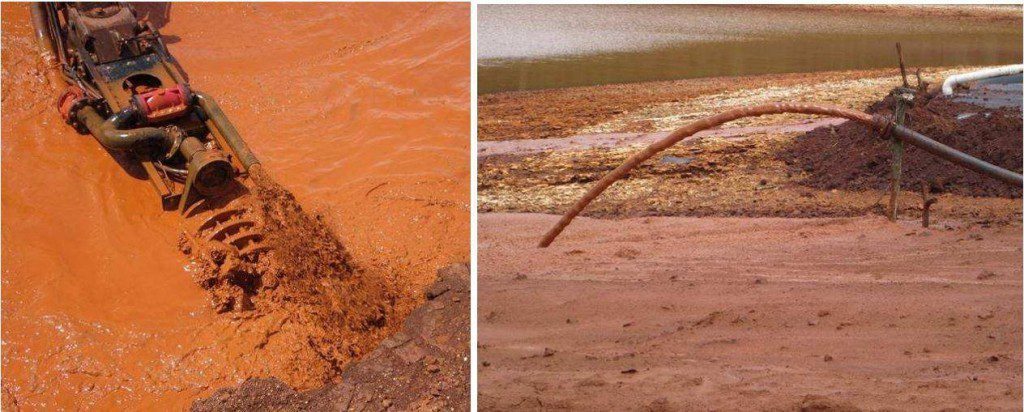

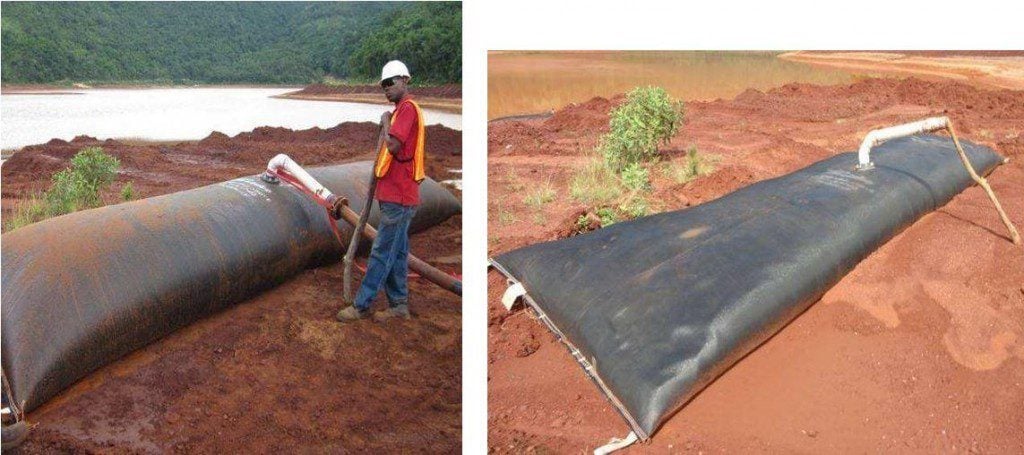
抽水泥流流出三千米软软软管流出六千米四千米HDPE管道内直径约87毫米(3.5米 ) 。 泥流排入原生泥沙滩约9%梯度泥流沉降时渐渐下降梯度。 时时流停止,泥流再积成波运动回流。 自然反移角比此少几度 — — 约5-6 % 。

泥头的剪裁强度极低,在振荡式液化上,挖掘两侧的强度足以站立近垂直2米。 即使是一夜之间,也有有限滑动,银行也可能因约0.5米割头/剖面程序而崩溃
水泵终止后,为冲刷管道,稀水泥泵打通直到线路清除开关系统接通水泵线3
4.2GETOBES
3Geotubes(1mx6m)填充用4Eddy泵泵的红泥填充率约30至40l/s,尽管难以评估,因为流和泥分不可见
Tube 1初始填充更多滑动泥和厚泥,泵运算符对条件有更好的感觉。管道填充至固态。第二管填充厚泥并填充持续至管道调试管道绑定并回填第二管并创建定义化床并限制相同旋转问题。相片5.7和5.8显示用池泥填的两根管子。除小漏两地管接触外,泥池池化成功

第三管定位于平面填充中流(但稳定厚度)泥巴并填充直到管子变肥
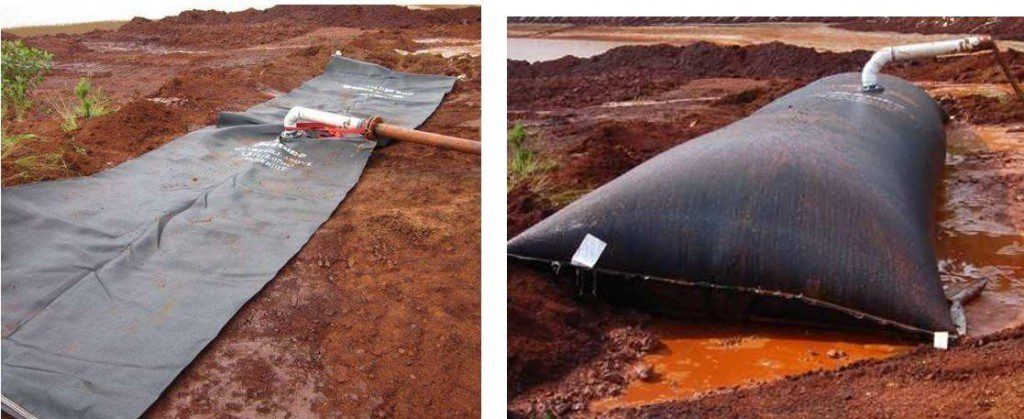

在所有三种情况中,都很少泥流或渗出管子。站上时,一些红水会挤出压力区。填充taut后,整包外装小红水滴表(照片5.11可见),但渗出泛泛标语
管子监听和最新照片摄取时间为2011年10月10日(填充后6周)显示管子因含泥脱水而体积下降。量损耗估计约30%。预期水分含量约达90%,固值约53%
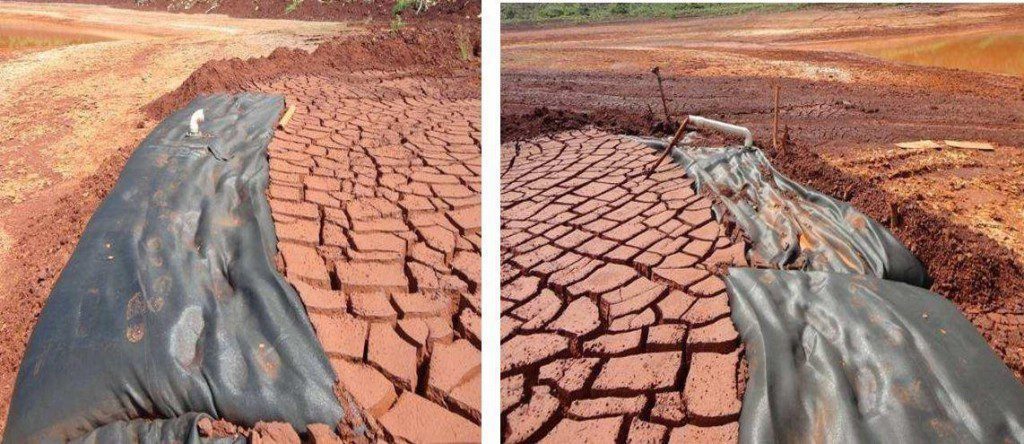


泥泵注入地球管后试验池中中厚至厚,大约37-40 % 。 6周后泥板不单固化,还用广深面裂缝大干涸,照片5.14和5.15中可见一斑。
管子和试验池监测工作正在进行中
6ext阶梯
审判证明:
- 泥可以抽水,但水需要加法实现正常排量
- 泥巴贴近地水分含量并极有可能按地水分含量抽取,如果泥巴鼓动更多并设计管道系统以减少摩擦损耗
- 泵需要铺设法,因为泥土太厚无法求素
- 泥面存取问题并难泵泥
因此,如果抽水法主要用于泥改池化,泵搭建至少需要以下内容:
- 能够访问泥面并高效安全地环游推荐用高强度绳索或钢电缆搭建浮舟。 泵系统应远程控制,因为这会限制人员在泥上正常移动
- 拥有不需池水的承接系统
- 能够激起吸头周围泥巴完全液化
- 拥有充量电量泵泥土近地或地表湿度并排出约1000米通软管线
从试验中还可以看出泥流不易滑动,因此需要两栖挖掘机松绑泵头周围的泥土,这种稀疏多液泥也有助于泵浮点运动,并限制浮点需要运动量,两栖挖掘机也可以向泵定位移动泥块
7PROGRAM程序
使用4号泥泵容量,泥移动大约需要1.5至2年时间,但泵需要更适合任务需要,目标周期为1年似乎合理,但在此之前,设备需采购并输入牙买加6和10英寸挖掘机泵附加件并正考虑提高GMP和更具攻击性完成时间轴的选项初步方案如下:
2011年12月-2012年3月:Procure泵和安斐挖掘机获取potoon编译牙买加
2012年4月-2012年5月:进口厂并现场搭建
2012年6月-2013年6月:泥泵和散装土工
2013年7月-2014年7月:地表稳定并启动植被





作业特题今日调用
和工程系商谈 并匹配合适的设备


